Our world is completely built on ideas. Every tool we use today, every device or piece of equipment was once an idea in someone’s head and once that person found the right method of execution, they transformed their idea or dream into a reality that, in turn, transformed the way the world functions. When I was a little boy in school, talking to someone through a mobile phone that you carry around was just a dream, and talking to people through watches was science fiction. Today, smartphones and smartwatches can perform these functions and many more. IoT is enabling devices to communicate with other devices! All of these achievements were possible due to the application of the right business model that made these ideas profitable to their creators.
Today, the world is filled with more brilliant ideas and dreams that can add value to certain customers and the world in general. These ideas may never get the opportunity to become a part of reality due to the lack of knowledge of the business model and how to monetize an idea.
In this article, I’m going to help you convert your idea into a successful sustainable business able to generate an income.
To achieve this ultimate goal, you need to learn how to build the business model components that will lead to your business monetization.
Business Model: Answering the Main Question
A business model is the most essential part of any business plan as it must provide the crucial answer to the question: what value will this business offer to the customer, and what is the target market?
To answer this question successfully and thoroughly, we have to focus on the separate business model components.
Business Model Components
As the name indicates the business model components are the building blocks of your business model that, when finalized and put together, will answer the big-picture question of how will your business be operated.
However, before getting into the individual business components, you have to start by understanding the main 3 categories which the business model components fall under to have an inclusive and comprehensive view of your project through the business model.
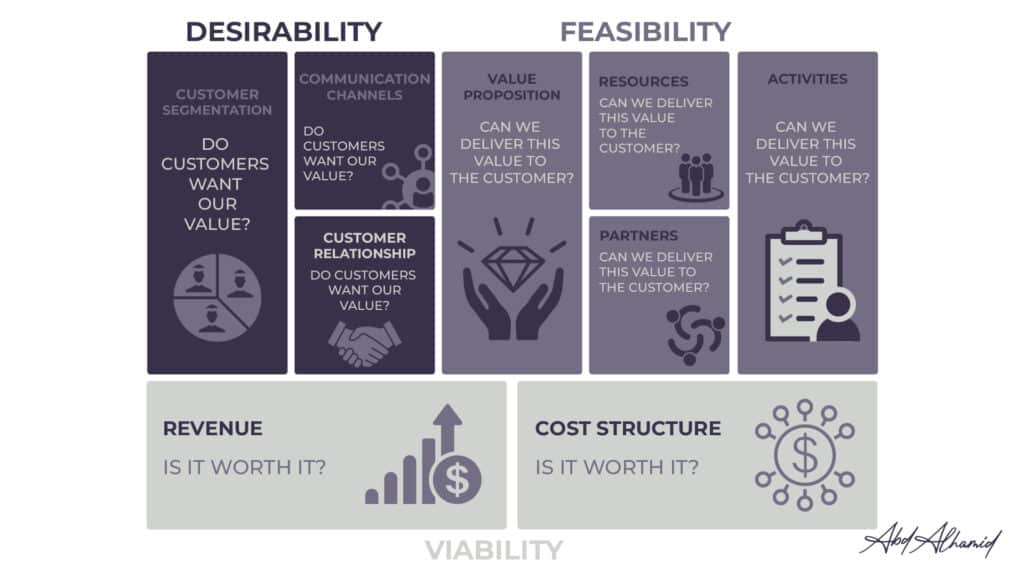
1- Desirability
As the name indicates, the desirability aspect of your business model represents desire; not your desire to create a product or launch the business, but rather the customer desire for the value that your business is going to offer whether it’s a product or a service. So, the main question of this aspect is: Do customers want our value?
There are many reasons why customers may reject your business’s value such as offering a product when the market is not ready for it despite how important the value is like offering a piece of tech that is too advanced for the customers’ needs as we saw with many of Google’s products.
As such, knowing and managing the customers and their needs through defining the customer segments, customer relationships, and communication channels is crucial not only to provide a high value and a competitive advantage but also to find the right balance in your offered value and avoiding going too far with the value that customers reject because it’s too much.
2- Feasibility
The feasibility aspect of the business model canvas answers the question: Can we do it? In other words, can you and your team deliver the promised value to the customers?
Many great ideas fail because of a lack of resources or the inability to find suitable partners to validate the business feasibility. This is why a great idea on its own is not enough. You have to follow through with carefully laying out and planning all the activities, resources, and partners as well as defining the value proposition of your project which means knowing the value that your future business is going to offer its customers, but more on that later. Now, all you need to understand is that feasibility in the business model will tell you whether the project can be done or not.
3- Viability
Finally, your business can be feasible (doable) and desired by customers, but is it worth it? The viability aspect of the business model canvas will answer this question. The ultimate goal of any business is to generate a profit and, as you know, profit is what you’re left with when you subtract the business costs from its revenue. The cost structure and revenue components of the business model will give you a good idea of what kind of profit your business can generate and, based on that, you can answer the business-worth question.
It’s a given that a business that is not profitable is not worth building. On the other hand, too little of a profit is also not worth it if you don’t have a clear vision of scalability to increase your business value and revenue as opposed to its expenses. So, you’ll have to know the viability line: What profit makes the business worth it for you, not only makes business sense.
Now that you have a clear idea of what the 3 main points or categories of the business model components are and what question each one should answer, let’s have a look at the individual business components.
1-Customer Segments

How to define your customer segments
In my opinion, customer segmentation is the most important component in any business model as it defines the target at which you’re directing the value offered by your business. There are several ways in which you can define your customer segments:
A. Customer segments can be based on demographics, psychographics (customer behavior), or geographic location among other options.
Your product can be designed for a specific age group, gender, people living in a certain location, or people with specific habits. For example, if your idea is to build a better way of making coffee, your product would be a new coffee maker, and your customer segment would be people who drink coffee (a behavior).
Mixing multiple options of customer segmentation will help you identify the perfect message to communicate with your potential customers to find the proper solution for them.
B. Another way to simplify your customer segmentation process is by defining the product users. Is this product going to be used by the masses, or will it target a specific narrow niche?
C. You can also approach your customer segments through focused segmentation, which is targeting one specific segment of customers, or diversified segmentation, which is targeting multiple segments at the same time. My recommendation is to stay focused on one single segment at the beginning of your business to avoid the massive confusion that diversified segmentation can create in a new business.
D. Finally, there is the multi-sided segmentation which is perfect for projects in the shared-economy sphere such as Uber and Airbnb. This segmentation focuses on both sides of the service, the service provider and the service buyer.
No matter which customer segmentation method works best for your business plan, this component should answer questions like the following:
- Who are the customers we’re offering value to?
- What are the characteristics of those customers? (needs, likes, dislikes, …etc)
- Do we have different types of customers? What are their classifications?
- Are we targeting the masses or a specific niche?
2- Value Proposition
The value proposition is supposed to show how your business is going to offer a different value compared to what’s already available in the market. The value proposition answers the question: what’s going to drive customers to buy your solution?
The first step to creating a value proposition is to define the problem the customer is facing and then present its solution.
Next, you must define the differentiator or the unique value of your solution, not the price. This is the competitive advantage that’s going to make the customer choose your solution over the traditional solution or any other option available in the market.
The differentiator may be how easy it is to use your solution, how fast it is delivered, or a specific feature that is not available in other solutions.
Once the value proposition component is complete, you should have answers to these questions:
- What is the value we’re trying to offer our customers?
- What is the problem that our value will solve for the customers?
- How will our business value be better than the competitors’ or any current solution for the same problem?
3- Channels
Now that you’ve defined your business target customer segment and the value differentiator proposition, you must determine the channels through which your business is going to communicate with customers.
In this section, we’re focusing on how to define the right channels for the right customer segment and customer phase as well as plan the integration between different channels and the elevation of the channels’ efficiency.
Customer Segments & Channels
Choosing the proper channels depends mainly on the characteristics of your customer segment and what media channels would work best for this specific segment. For example, back when the main competition in shared transportation in the MENA region was only between Uber, as an international service provider, and Careem, as the regional service provider, it was evident that Careem was crushing the Channels game as it was designed and run by local people from the region familiar with the culture. Careem understood that customers in the MENA region preferred to get customer service over the phone. Meanwhile, Uber was struggling on that front as it provided customer service via email and the app itself.
Integrating Channels
Of course, there are multiple channels of communication between a business and its customers such as CRM, social media platforms, phones, email, and the business app, to name a few. For your channels to function successfully, you must find the best way to integrate those channels to show your customers that your business is always connected and avoid lost communications from one medium to another.
Customer Phase & Channels
You must choose the proper channel depending on the phase your customer is in. For example, communicating with a lead or a potential customer whom you’re looking to onboard is going to be different from communicating with a customer who already bought your service or product and needs assistance from customer support.
Defining those different channels based on the customer phase in the business model will save you time, effort, and money in the future of your business keeping in mind that you can always pivot.
Channels Efficiency
Your business model must also measure and ensure the efficiency of the chosen channels not only in communicating with the customer but in solving the customers’ problems as well.
An example of poor channel efficiency is using an online-based channel like email or a chatbot in a rural area where the internet is known to be unstable, especially in regions like Africa.
After covering all of these aspects of the channels component, your business model should provide answers to these questions:
- How will you reach potential customers to propose your business’s value to them?
- How will your value be delivered to your customers?
- How will you efficiently use your channels to justify their costs?
4- Customer Relationship

Cultivating a good relationship between your business and its customer is essential for business growth and sustainability. A loyal customer will promote your business and brand through word of mouth which will get you more customers. This is why you must define your customer relationship in the business model.
One of the first factors of the customer relationship that you need to define in the business model is the user experience. Designing your business in a way that provides the best user experience will go a long way in maintaining the relationship.
Another aspect of your business’s relationship with its customers is how to handle a complaint. Uber for example responds to complaints by sending an apologetic message and adding a small amount of money to the customer’s wallet as an apology gift.
While this is a good way to give your customers a gift and increase the likelihood of the same customer using your service again to benefit from the wallet credit, this method would not be good for refunds. Many customers might view app credit or store credit as a bad way for refunds as they might just want to get their money back and not use it in your business.
Including a humanization aspect in the customer relationship management plan goes a long way in building this relationship. My research showed a huge difference in customer loyalty when there’s a human personal aspect to the service.
For example, customers who enter a coffee shop and get a number to receive their coffee have a completely different experience from those who give their names and get personalized coffee cups with their names on them.
Finally, focus on your front-line teams, such as sales and support, to make sure these teams have the tools to show the customers that this business is always ready to assist and, more importantly, is happy to do so.
Such matters can greatly affect your brand image and customer loyalty. So, it’s important to decide on these details in your business model and provide accurate answers to the following questions:
- How will the business deal with different customer segments?
- How often will the business communicate with customers?
- What type of relationship will your business maintain with its customers? (Focus on humanization)
- How often does the business provide customers with support?
5- Revenue
Now we arrived at the reason or the goal of building a business in the first place. Generating revenue is the ultimate goal of your business whether this revenue is going to be a profit for stakeholders or it’s for sustaining the business if your organization is non-profit.
While it’s acceptable for a business to initially focus on a single revenue stream, your business model must include the different revenue streams that you plan to branch out into in the future.
In the business model, you must define your revenue-generating points. These points will be determined by answering these questions:
- What will your customers pay for? What methods will the business use to generate revenue?
- What are the payment methods and financing plan your customers will use?
- What are your business payment terms, cancellation, and return policies?
- How will the revenue create a stable income for the business?
- What future revenue streams do you plan to create in the future to scale your business?
- What are the pricing strategies your business is following?
6- Resources

Your business model must define all the resources that your business needs to start and grow in the market. Resources must include every single thing needed to provide your customers with value whether it’s a product or a service.
These resources can be a combination of tangible and non-tangible resources such as building a factory vs. building software or a website for your business. Resources also include the team that you need to hire to deliver the required value. For example, you might need to hire software developers to deliver the business app, delivery personnel, and customer service representatives.
Of course, the most important and most noticeable aspect of the resources is the fund that’s going to make the business possible to exist in the first place. Your business model must define the initial fund require to kick off the project and the source of this fund.
To cover all the resources of your business, you must answer these questions:
- Specify all the required assets to deliver the value from the value proposition
- What are the non-tangible resources required to deliver the value?
- Specify the required human resources to deliver the value.
- Where will your funds come from? (financial resources)
7-Activities
This is a huge and important component of any business model as it revolves around the process and operations of the business.in other words, the key activities component is all the actions that much be taken for your business to function. This component must list and detail all the required activities to deliver the promised value to the customer segments. The activities component must define your business’s every move from building and maintaining a website or factory, for example, to delivering the product or performing the service for the customer.
In addition to focusing on the processes and operations of your business, the activities component of the business model should also include how your business will handle and solve problems within the operations when they occur and how will the business identify the source of these problems. The way to solve an internal problem in the manufacturing process, for example, must be different from solving a problem that a customer is facing with the product.
Answering the How questions will lead you to define the actions necessary to build and run every aspect of your business.
- How will the business operations run?
- How will the business deliver value to customers?
- How will the business manage the production process?
8-Partners
The partners component must define every outer entity that’s going to help your business provide value to its customers from suppliers to software and HR companies if you choose to outsource those departments for example.
Defining the partners component will help you build an optimized business and avoid having a bloated system that can be a nightmare to manage, therefore, allowing you more space to focus on the business’s core values and core operations which will eventually lead the business to grow.
For example, instead of having to hire and manage several teams consisting of 100 members, you can simply hire the core team consisting of 10-20 people and outsource the rest which will reduce your cost and your business risk.
Defining the partner component correctly will create a win-win situation for you and your partners and increase market penetration for all parties.
The partners component of your business model must cover every party outside your company involved in the business activities. So, make sure to provide answers to these questions:
- Who are your business partners?
- What activities will your business outsource to partners?
- What resources come from your partners?
- What validates choosing a specific partner in terms of value and cost?
9-Cost
The cost component should not just focus on the numbers, but its main focus must be the cost structure. Define the individual cost points that the business requires. Differentiate between fixed and variable costs. Define your scaling costs in terms of penetrating new market segments, expanding to new countries, and how will it affect your business cost structure.
You must also define your asset structure. Will your business use a heavy asset structure, meaning that the business will own the assets, or will it follow a light asset structure by renting the assets or even use a shared-economy asset such as in the Uber and Careem model?
The main questions that the cost component must answer are:
- What is your business’s essential cost structure? Does it need optimization?
- What is the cause for each cost point?
- How are the business resources, partners, and activities connected to your cost structure?
- Define your business’s fixed costs vs. variable costs
Conclusion
Once you defined the nine components of the business model, you will have the most essential part of your business plan ready with a clear vision of every aspect of your business. While you might have a general idea of how every aspect of the business will work, putting the business model on paper in detail will first help you to clarify the fine details and, secondly, help you explain your business to your team, potential investors, and other interested parties.
Working on a business model may seem like a daunting process, but once you understand the components and their requirements, you can get the famous business model canvas and start filling the template by answering the provided questions to make the image clear.




